Report Data Contexts are used to drive and build Report output content and also allows the consolidation and integration of data from multiple different sources and types such as API's, websites, databases and data files.
Named Data Contexts are shared throughout the Report and allow data in XML documents to be contextually enumerated. Multiple Report Data Contexts can be added and used throughout a Report.
Context types can be XQuery, Python, XML, CSV, JSon, XLSX, HTML, MS SQL, MySQL, MDB, ODBC and OLEDB Data Sources that can be read and used in the Report.
To add or edit a Report Data Context click the menu Data | Report Data Contexts or select the Data Contexts (...) collection button from the Report property page.
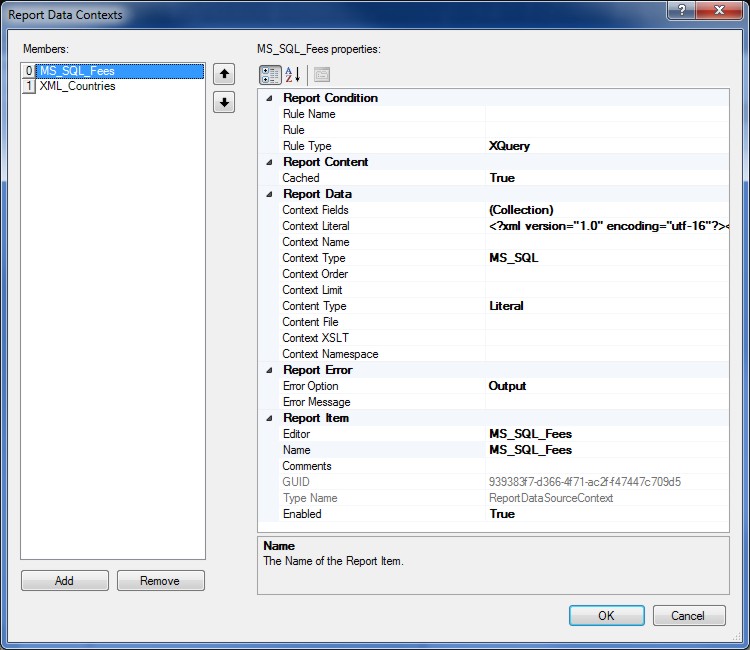
The default Data Context is the Report Data Source (XDM) root node and if no Data Context is specified then the current Report Data Source will be used.
After a Report Data Context has been applied the Report Design the must be refreshed or reloaded to ensure all elements are updated.
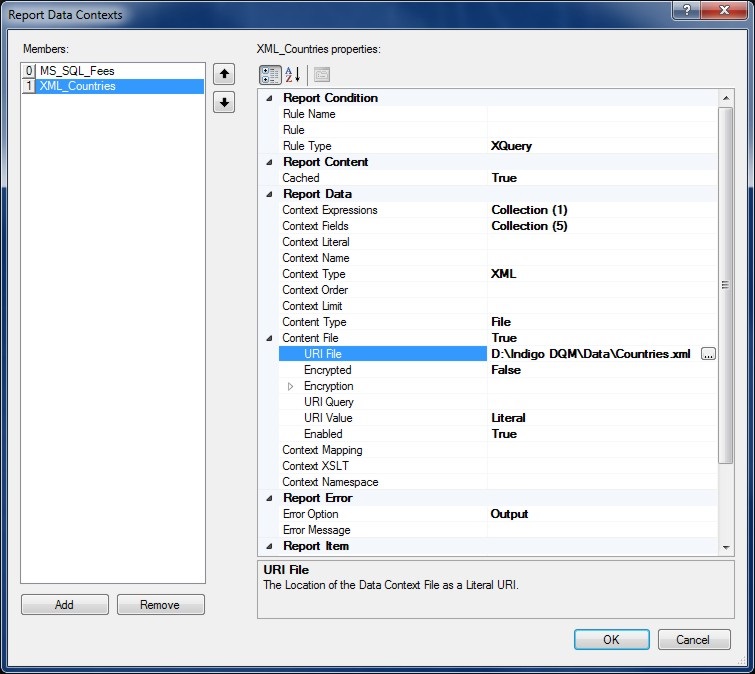
Named Data Contexts are applied to Report elements by setting the Context Source to Named. The Context Name will then be available in the drop-down list for the Report element.
Report Data Contexts exported using the Export Wizard can also be reused as a shared Resource File by setting the File property of the Data Contexts File to the exported or saved RDL content.
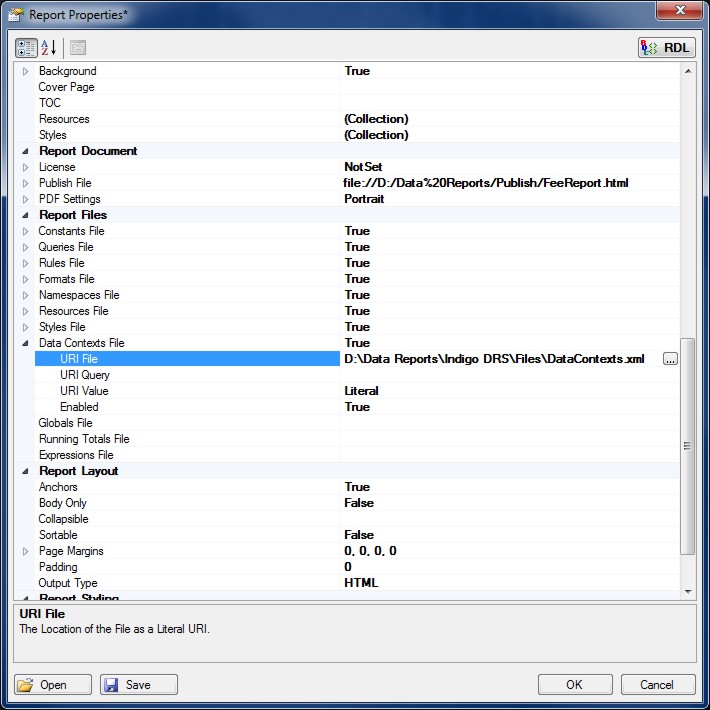
Click the Data Contexts File (...) property button to specify the URI File or URI Query for shared Report Data Contexts.
Data AI / Machine Learning*
Data Contexts can use Python for Machine Learning / AI and Statistical Modelling. An optional add-in software component for Indigo DRS facilitates the use of the Accord .NET Framework for Machine Learning and enhances the presentation and formatting of data making it suitable for enhanced reporting.
Context Sources
Context Sources specify that a Data Context is applied to either a specific local Report element or be named Data Context that can be shared throughout the Report. Set the Context Source to Local to apply the Data Context to the current Report element or Named if it is a shared Report Data Source Context. Named Data Source Contexts can be selected from the Context Name drop-down.
If a Data Context is to be used more than once it is recommend that a shared named Data Context be created with caching enabled.
Context Types
Data Contexts can be either a series of XQuery or Python statements as applied to the current Data Context or XML, CSV, JSon, XLSX, HTML, MS SQL, MySQL, MDB, ODBC and OLEDB Data Sources.
XQuery and Python statements are evaluated in the current Report Data Context. Context Types that are XML, JSon, CSV, XLSX or HTML are read from the File URI or database.
Content Types
The Report Data Context Content Type can be either a Literal or a File. If the Content Type is a File for the Report Data Context then it is read from the specified File URI.
File URI's
Report File URI's are expressed as Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI) and can be either a Literal or a Query to specify the location of the File Resource. Literal values are constants that are determined by the URI File property.
Query based URI's are determined by the result of the URI Query which can be a series of XQuery or Python statements to specify the location of the File URI.
Report Caching
Report elements can cached to improve the speed and performance of Report builds. Caching stores a copy in memory of frequently used content instead of reading the file directly from disk.
Report Namespaces are used for providing uniquely named elements and attributes and is a mechanism to avoid name conflicts by differentiating elements or attributes within an XML document that may have identical names, but different definitions. If the Report Data Source contains namespaces they can be applied to the XQuery Processor.
NOTE: *Optional features that require a separate licensing entitlement to be purchased!

